Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Toigawa, Tomohiro; Kumagai, Yuta; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Ban, Yasutoshi; Matsumura, Tatsuro
UTNL-R-0502 (Internet), 2 Pages, 2022/04
This report summarizes the results obtained in FY2020 at the Electron Linac Facility of the University of Tokyo. The radiolysis process of 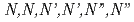 -hexaoctyl nitrilotriacetamide (HONTA), which is expected to be used as an extractant in a separation process for minor actinides, diluted in dodecane was investigated by pulse radiolysis experiments. The radical cation and the triplet-excited state of HONTA were observed in the nanosecond time region. The transition from the radical cation to the triplet excited state was slowed down by adding electron scavengers, and further, the reactivity of the triplet excited state was also suppressed.
-hexaoctyl nitrilotriacetamide (HONTA), which is expected to be used as an extractant in a separation process for minor actinides, diluted in dodecane was investigated by pulse radiolysis experiments. The radical cation and the triplet-excited state of HONTA were observed in the nanosecond time region. The transition from the radical cation to the triplet excited state was slowed down by adding electron scavengers, and further, the reactivity of the triplet excited state was also suppressed.
Hata, Kuniki; Urushibara, Ayumi*; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Lin, M.*; Muroya, Yusa*; Shikazono, Naoya; Yokoya, Akinari; Fu, H.*; Katsumura, Yosuke*
Journal of Radiation Research, 56(1), p.59 - 66, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:29.49(Biology)Hirade, Tetsuya
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 76(2), p.84 - 89, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:25.42(Chemistry, Physical)There are many connections between radiation and positronium chemistry. The Spur Reaction model proposed by Mogensen needs much radiation chemistry knowledge. On the other hand, the Spur Reaction model could give new ideas to radiation chemists. Positronium formation reaction is very fast and hence there is a good relationship between reactions observed by a pulse radiolysis measurement and positronium formation, which was shown by Dupratre et al. Enhancement of positronium formation at low temperatures was successfully explained by the reaction of trapped electrons and positrons. The trapped electrons have been studied well by radiation chemists. That knowledge was needed to propose a new idea to explain the positronium formation at low temperatures. And now, probably it is becoming possible to use the positronum formation reaction to study the trapped electrons. Positron methods will be able to be used for the radiation chemistry research.
Yoshida, Yoichi*; Yang, J.*; Saeki, Akinori*; Tagawa, Seiichi*; Shibata, Hiromi*; Namba, Hideki; Kojima, Takuji; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
JAERI-Review 2004-025, TIARA Annual Report 2003, p.143 - 144, 2004/11
no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Yoichi*; Yang, J.*; Seki, Shuhei*; Saeki, Akinori*; Tagawa, Seiichi*; Shibata, Hiromi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kojima, Takuji; Namba, Hideki
JAERI-Review 2003-033, TIARA Annual Report 2002, p.145 - 146, 2003/11
no abstracts in English
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kimura, Takaumi; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Kozawa, Takahiro*; Tagawa, Seiichi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 106(39), p.9036 - 9041, 2002/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:8.63(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
; Namba, Hideki; Aoki, Yasushi; Watanabe, Ritsuko*; *; Watanabe, Hiroshi
JAERI-Tech 96-046, 65 Pages, 1996/11
no abstracts in English
*
PNC TJ1602 96-002, 129 Pages, 1996/02
Since a chloride ion is assumed to be one of the predominant solutes dissolved in groundwater, a study of the radiolysis of chloride ion and oxychlorides in aqueous solutions has been carried out in order to obtain the reliable and predictable data for the understanding the radiation induced reactions taking place in groundwater, relevant to the geological radioactive waste repository. The rate constants of the reactions between water decomposition products and different oxychlorides were determined by means of pulse radiolysis and laser photolysis methods. By using the techniques of photometry and ion-chromatography, the products formed by irradiation were analyzed and the overall reactions were summarized. After the comparison between the simulation and the experimental results, the redox reactions of the oxychloride compounds in aqueous solution were summarized and future work to be done has been pointed out.
 , He
, He
 , C
, C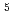
 and Ne
and Ne
 ions
ionsIwamatsu, Kazuhiro; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kimura, Atsushi; Kurashima, Satoshi; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
Heavy ion beams, one of the high linear energy transfer (LET) radiations induce specific irradiation effects which are different from those of low LET radiations. The effects are attributed to heterogeneous distribution of reactive species along their trajectories, so called "track structure". Water was selected as target in this study because more data exist for radiolysis than any other substances. Hydroxyl radical (OH), one of the most important water decomposition species, was focused on by using bromide ion as a probing reagent, and their reactions were observed by the ion beam pulse radiolysis system. The formation and decay of Br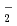 were observed at 375 nm (
were observed at 375 nm ( [Br
[Br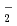 ] = 9000 M
] = 9000 M
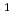 cm
cm
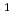 ). The formation chemical yield of it after pulse irradiation decreased with increasing atomic numbers of the incident ions. Radical recombination reaction occurs easier by higher LET ions because of denser radical formations. Therefore, the decrease in the yields of OH scavenged by Br
). The formation chemical yield of it after pulse irradiation decreased with increasing atomic numbers of the incident ions. Radical recombination reaction occurs easier by higher LET ions because of denser radical formations. Therefore, the decrease in the yields of OH scavenged by Br induces the decrease in the chemical yields of Br
induces the decrease in the chemical yields of Br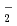 . The decay rates of the chemical yields increased with the atomic mass of the ions. The concentrations depend on the dose rate and chemical yield, and the dose rates proportional to LET value. The concentrations after pulse increased with increase in the atomic mass of the ions and resulted in faster decay in heavier ions.
. The decay rates of the chemical yields increased with the atomic mass of the ions. The concentrations depend on the dose rate and chemical yield, and the dose rates proportional to LET value. The concentrations after pulse increased with increase in the atomic mass of the ions and resulted in faster decay in heavier ions.
Hata, Kuniki; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Muroya, Yusa*; Katsumura, Yosuke*; Hanawa, Satoshi; Kasahara, Shigeki; Tsukada, Takashi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kondo, Takafumi*; Godo, Masao*; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Inoue, Masao
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 retention with changing hydrophilicity of carbonate slurry, 2; Pulse radiolysis measurement of local (partial) viscosity of pore water
retention with changing hydrophilicity of carbonate slurry, 2; Pulse radiolysis measurement of local (partial) viscosity of pore waterNagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*; Ito, Tatsuya; Godo, Masao*; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Tamaki, Ryoya*
no journal, ,
Hydrogen molecules (H ) retained by highly viscous suspension such as a carbonate slurry exist in the pore water of suspension in the form of gas (bubble). The H
) retained by highly viscous suspension such as a carbonate slurry exist in the pore water of suspension in the form of gas (bubble). The H behaviors such as the reaction of dissolved species of H
behaviors such as the reaction of dissolved species of H and the process forming H
and the process forming H bubble are mainly determined by the viscosity of pore water, while the H
bubble are mainly determined by the viscosity of pore water, while the H retention by the macroscopic viscosity of suspension. Such local (partial) viscosity is generally unclear. In order to clarify the H
retention by the macroscopic viscosity of suspension. Such local (partial) viscosity is generally unclear. In order to clarify the H retention/release mechanism in the suspension, it is important to estimate this viscosity. In this report as the second in a series of presentations, the reaction (decay) rate of hydrated electrons (e
retention/release mechanism in the suspension, it is important to estimate this viscosity. In this report as the second in a series of presentations, the reaction (decay) rate of hydrated electrons (e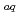
 ) formed as a radiolysis radical of pore water was transiently measured by using ns-pulse radiolysis, and the viscosity of pore water was estimated for the current and hydrophilicity-lowered slurries to be compared with each other.
) formed as a radiolysis radical of pore water was transiently measured by using ns-pulse radiolysis, and the viscosity of pore water was estimated for the current and hydrophilicity-lowered slurries to be compared with each other.